Prof. Jiuxing Jiang's group at School of Chemistry developed an extra-large pore zeolite with unprecedented 24-ring channels using traditional Chinese medicine
Source: School of Chemistry
Written by: School of Chemistry
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
Extra-large pore zeolites are especially attractive due to the industrial demands of shape-selective catalysis and adsorption for large molecules. Among the 235 known zeolite structures, extra-large pore zeolites are still rare. It is challenging to synthesize zeolites with more than 20-ring opening. The usage of the pre-designed organic structure directing agents (OSDAs) is the most effective synthetic strategy to synthesize these materials. However, such OSDAs are rarely commercially available and very expensive. On the other hand, quinolizidine alkaloids with unique molecular skeletons are affordable and easy to modify to produce novel OSDAs, which may lead to some novel and specific extra-large pore zeolite structures. Fortunately, we have prepared three extra-large pore zeolites ITQ-37, ITQ-43 and SYSU-3 (Sun Yat-sen University no. 3) by using simply modified sophora alkaloids. Among them, SYSU-3 represents a new zeolite structure.
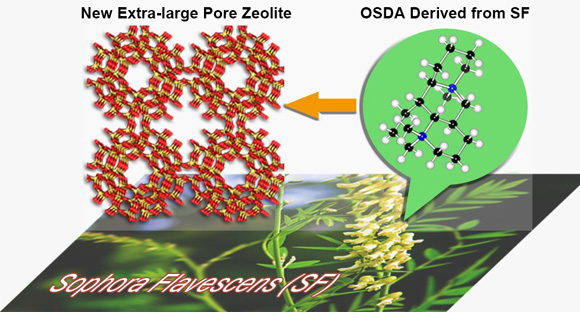
Sophora alkaloids can be used as OSDAs for synthesizing new zeolite with unprecedented 24-ring opening.
Continuous rotation electron diffraction (cRED) method have been successful in structure determination for nanosized crystals. The structure of SYSU-3 was solved and refined using cRED data. SYSU-3 presents a new zeolite framework topology with the first 24 × 8 × 8 -ring extra-large pore system, which may offer unique shape selectivity and allow reactions involving large species. It was noteworthy that the unique skeleton of the OSDA plays an essential role in the formation of the distinctive zeolite structure. This work lights up new perspective for developing newextra-large pore and mesoporousmaterials by using alkaloids as OSDAs. The related work has been published on Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6486-6490. (selected as Inside Cover).
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences.
Link to the article: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.201801386
Link to the cover: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/anie.201803954
