Source: Cancer Center
Written by: Cancer Center
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
The gastroenterological cancer research team led by Rui-Hua Xu, President and Professor of State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, published an original research article entitled “Modulation of Redox Homeostasis by Inhibition of MTHFD2 in Colorectal Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications” (online first) in the
Journal of National Cancer Institute (IF 2018=11.23). Rui-Hua Xu is the corresponding author and Huai-Qiang Ju, an associate professor from his team, is the first author.
Overcoming oxidative stress is a critical step for tumor progression, however the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. The folate metabolism pathway produces one-carbon formyl groups for various cellular processes, including
de novo purine and thymidine synthesis, which are necessary for cell proliferation, not typically considered as an important NADPH source. In this pathway, MTHFD2 can generate NADPH from NADP+, suggesting it may play critical roles in cellular detoxification. As illustrated in Figure 1, in this study, Ju et al. report that the overexpressed NADP-dependent enzyme MTHFD2 is correlated with colorectal cancer (CRC) poor prognosis. At biochemical level, MTHFD2 predominantly maintains intracellular NADPH homeostasis and promotes CRC cell survival under stress conditions such as hypoxia or anchorage independence. Mechanistically, mutant Kras transcriptionally upregulates MTHFD2 expression via c-Myc activated by the Akt and ERK pathways. Importantly, genetical or pharmacological inhibition of MTHFD2 by its novel inhibitor LY345899 significantly suppresses CRC tumorigenesis and metastasis in cell based xenografts and PDX models. This study highlights the crucial roles of MTHFD2 in redox regulation and CRC progression, thus raises the therapeutic implications. For the first time, this study demonstrate that MTHFD2 inhibitor LY345899 is a highly effective therapeutic compound with reduced toxicity for CRC treatment. Future study should focus on the development of more effective and selective inhibitors for MTHFD2, testing their effects in pre-clinical and clinical trials and the combinatorial effects with clinical chemotherapy drugs.
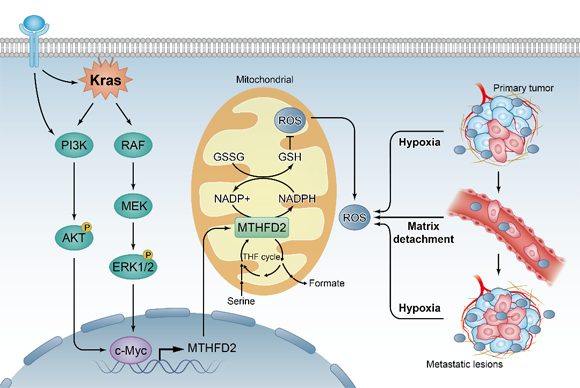
Figure 1. Proposed working model of this study
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China and Guangdong Natural Science Foundation.
Link to the paper:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30534944



