Source: The Third Affiliated Hospital
Written by: The Third Affiliated Hospital
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
Recently, noninvasive diagnosis of antibody-mediated renal allograft rejection has been successfully achieved. Through synthesizing the C4d-targeted microbubbles, Professor Qiquan Sun and Professor Jie Ren from The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University have successfully realized the non-invasive diagnosis of antibody-mediated rejection (AMR). The utility of this approach potentially prevents patients from going to have to undergo invasive biopsies in clinic, and promote the development of medicine.
AMR has emerged as a major cause of renal allograft dysfunction, which resulted in approximately 60% of graft dysfunction in renal transplants. C4d, a degradation product of complement activation, is recognized as the specific diagnostic marker of AMR. However, currently, C4d detection is dependent upon tissue biopsy, which is invasive and provides only local semi-quantitative data.
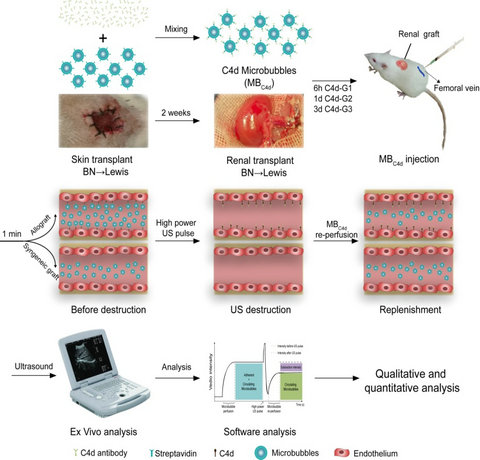
The procedure for C4d-targeted ultrasound (US) imaging in a rat model of renal antibody-mediated rejection (AMR)
Targeted ultrasound imaging has been used extensively for noninvasive and real-time molecular detection with advantages of high specificity and sensitivity. In this study, Professor Sun designed C4d-targeted microbubbles using a streptavidin-biotin conjugated method and detected C4d deposition in vivo in a rat model of AMR by enhanced ultrasound imaging. This noninvasive procedure allowed successful acquisition of the first qualitative image of C4d deposition in a wide renal allograft section, which reflected real-time C4d distribution in grafts. Moreover, Professor Sun and his team introduced normal intensity difference for quantitative analysis, which exhibited a nearly linear correlation with the grade of C4d deposition according to pathologic analysis. In conclusion, this study reported a noninvasive, comprehensive, and quantitative method for detecting C4d deposition in renal allografts through targeted US imaging.
The research results, titled “Noninvasive quantification of intrarenal allograft C4d deposition with targeted ultrasound imaging”, was published in the top journal of transplantation area Am J Transplant in September.
Link to the paper: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30171802



