Source: School of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Written by: School of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
The research group of Prof. Peiqing Liu and Min Li at School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University published a paper entitled “Discovery of a small molecule targeting autophagy via ATG4B inhibition and cell death of colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo” in Autophagy (IF=11.10) on September 20th, 2018.
The cysteine protease ATG4B is a key component for autophagy, which is a cellular catabolic pathway involved in energy balance. To help further explore ATG4B functions and potential therapeutic applications, this study integrated in silico screening and in vitro assays to discover a potent ATG4B inhibitor, named S130. Here, the researchers found that S130 did not cause the impairment of autophagosome fusion, instead, S130 might attenuate the delipidation of LC3-II on the autolysosomes to suppress the recycling of LC3-I. Intriguingly, S130 induced cell death, which was accompanied with autophagy stress and could be further exacerbated by nutrient deprivation. Such cytotoxicity could be partially reversed by enhancing ATG4B activity, suggesting that ATG4B may be important for cancer biology. Meanwhile, S130 was distributed in tumor tissues in vivo and was also effective in arresting the growth of colorectal cancer cells. Thus, this study indicates that ATG4B is a potential anticancer target and S130 might be a novel small-molecule candidate for future cancer therapy.
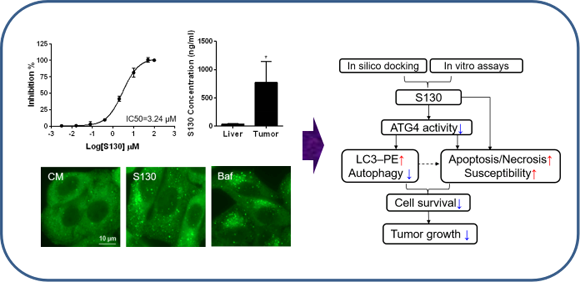
Illustration of the screening strategy for ATG4B inhibitors and the proposed anti-tumor mechanisms of S130
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671437), the National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2017ZX09305010), and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2016A030313335).
Link to the article: https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1517073



