Source: The First Affiliated Hospital
Written by: The First Affiliated Hospital
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
Recently, Professor Deng Yubin’s team in the Research Center of Translational Medicine of The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University has synthetised specific lipase-responsive polymer-coated gadolinium nanoparticles for early diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. The related research results were published in the international famous journal
Biomaterials in the field of biological materials.
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a kind of severe acute abdomen which has a high fatality rate, and the incidence of the disease is on the rise. Currently, available methods for diagnosis of AP are mainly dependent on serum enzyme analysis and imaging techniques that are too low in sensitivity and specificity to accurately and promptly diagnose AP. The lack of early diagnostic tools highlights the need to search for a highly effective and specific diagnostic method. MRI is considered to be one of the most promising method for early diagnosis of AP, but there is still no available MRI contrast agent for early diagnosis of AP clinically.
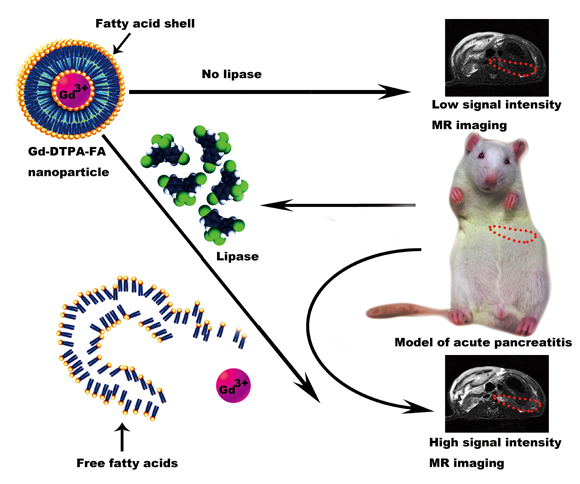
For the above scientific problems, Professor Deng Yubin’s team adopted the strategy of lipase enzyme activation and synthesized a conditionally activated, gadolinium-containing, nanoparticle-based MRI nanoprobe (Gd-DTPA-FA) as a diagnostic tool for the early identification of AP, which exhibited low cytotoxicity and excellent biocompatibility
in vitro and
in vivo studies. L-arginine induced a gradual increase in the intensity of the T1-weighted MRI signal from 1h to 36h in AP rat models. The increase in signal intensity was most significant at 1h, 6h and 12h. These results suggest that the Gd-DTPA-FA as a MRI contrast agent is highly efficient and specific to detect early AP.
The study showed the application potential of the nanomaterials in the specific and early diagnosis of AP. It would not only offer a new method for clinical diagnosis of AP, but also be expected to improve the early diagnostic rate of AP. The work was achieved by the Research Center of Translational Medicine, the Department of Interventional Radiology of The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University and the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Sun Yat-sen University.
The related research paper entitled “Specific lipase-responsive polymer-coated gadolinium nanoparticles for MR imaging of early acute pancreatitis” was published in the latest biomaterials authoritative journal
Biomaterials (IF: 7.604) (PMID: 24103651)(The authors: Hong-Wu Zhang, Li-Qin Wang, Qing-Feng Xiang, Qian Zhong, Lu-Ming Chen, Cai-Xia Xu, Xian-Hong Xiang, Bo Xu, Fei Meng, Yi-Qian Wan, David Y.B. Deng) . The present research project is one of the research projects supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China and the Ministry of Education of Guangdong Province University-Industry Cooperation Project.
This was the third of the three papers with Professor Deng Yubin as corresponding author that were published consecutively in
Biomaterials since 2012 (
Biomaterials 2012, 33; IF: 7.882 and
Biomaterials, 2013, 34; IF: 7.404). The research on novel nanomaterials for early diagnosis of AP has gained high recognition and affirmation from the international peer experts for the nanomaterials translational medicine application research of Sun Yat-sen University. Professor Deng Yubin was also invited as a reviewer of the journal
Biomaterials.
 Biomaterials
Biomaterials, 2012, 33
 Biomaterials
Biomaterials, 2013, 34
 Biomaterials
Biomaterials, 2014, 35
Related link:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Specific+lipase-responsive+polymer-coated+gadolinium+nanoparticles+for+MR+imaging+of+early+acute+pancreatitis



